Enhancing Healthcare Excellence: The Role of Total Quality Management in Hospital Management
- islam Arid

- Feb 5, 2024
- 3 min read
Updated: May 15, 2024

Introduction:
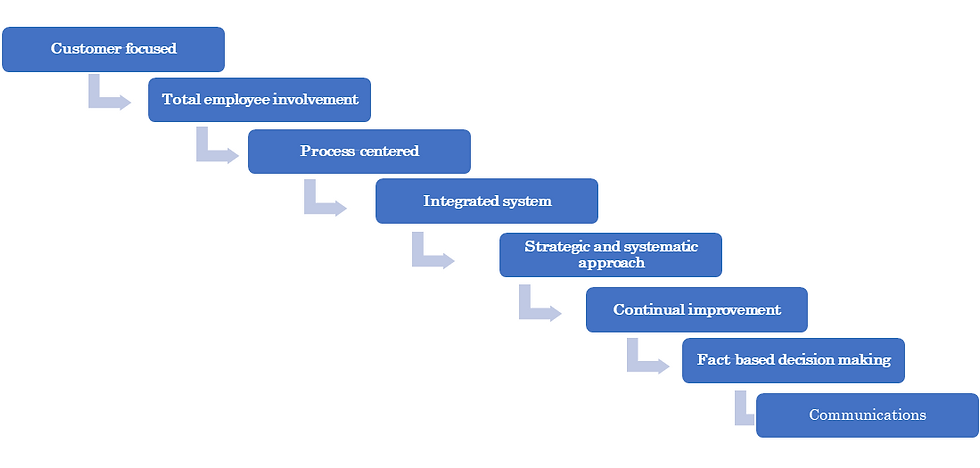
Total Quality Management (TQM) has become a cornerstone in the pursuit of excellence within healthcare organizations, especially in the context of hospital management. This comprehensive approach focuses on continuous improvement, emphasizing patient-centric care, streamlined processes, employee involvement, data-driven decision-making, and preventive measures. In this article, we delve into the key applications of TQM in hospital management, accompanied by real-world examples.
1. Patient-Centered Care:
TQM emphasizes a patient-centric approach, focusing on meeting and exceeding patient expectations.
Regular feedback from patients is collected and analyzed to identify areas for improvement.
Continuous efforts are made to enhance the overall patient experience, including communication, responsiveness, and satisfaction.
Example:
TQM places a strong emphasis on delivering patient-centered care, aiming to meet and exceed patient expectations. One notable example is the Cleveland Clinic, which has consistently ranked among the top hospitals in the United States for patient satisfaction. The clinic actively collects and analyzes feedback from patients, using this information to make informed decisions and enhance the overall patient experience. Through initiatives like personalized care plans and improved communication channels, the Cleveland Clinic exemplifies TQM principles in patient-centric care.
2. Process Improvement:
TQM involves the identification and analysis of key processes within the hospital, from admission to discharge.
Streamlining processes helps in reducing errors, minimizing delays, and improving overall efficiency.
Continuous process improvement methodologies, such as Six Sigma, are often integrated into TQM practices to eliminate defects and enhance quality.
Example:
Identifying and analyzing key processes within a hospital is integral to TQM. A shining example is the application of Six Sigma methodologies at Virginia Mason Medical Center. By employing process improvement techniques, Virginia Mason reduced patient wait times, enhanced the accuracy of diagnoses, and improved overall operational efficiency. TQM, integrated with Six Sigma, helps organizations like Virginia Mason continuously refine their processes, resulting in better outcomes for both patients and staff.
Our courses :
3. Employee Involvement and Training:
TQM recognizes the importance of involving all staff in the pursuit of quality improvement.
Staff members are trained to understand their roles in maintaining and improving quality standards.
Teams are formed to address specific quality issues, fostering a culture of collaboration and shared responsibility.
Example:
Recognizing the pivotal role of every staff member, TQM fosters a culture of collaboration and shared responsibility. The Mayo Clinic is renowned for its commitment to employee involvement. Through continuous training programs and the formation of quality improvement teams, Mayo Clinic empowers its staff to actively contribute to maintaining and improving quality standards. This inclusive approach enhances employee morale, leading to a positive impact on patient care and organizational performance.
4. Data-Driven Decision Making:
TQM relies on data and metrics to monitor and measure performance.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are established to assess various aspects of hospital operations, such as patient outcomes, waiting times, and infection rates.
Data analysis guides decision-making processes and helps identify areas requiring attention and improvement.
Example:
TQM relies on data and metrics to monitor and measure performance effectively. The Massachusetts General Hospital is a prime example of leveraging data-driven decision-making. By establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) related to patient outcomes, waiting times, and infection rates, the hospital can swiftly identify areas requiring attention and improvement. The integration of data analytics into TQM practices at Massachusetts General Hospital exemplifies the power of informed decision-making for sustained quality improvement.
5. Preventive Measures and Risk Management:
TQM encourages the implementation of preventive measures to avoid errors and adverse events.
Risk management strategies (including disaster management) are developed to identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks in patient care and organizational processes.
Example:
TQM encourages a proactive approach to prevent errors and adverse events, aligning closely with effective risk management strategies. The Johns Hopkins Hospital, for instance, implements comprehensive risk management protocols to identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks in patient care and organizational processes. By incorporating disaster management plans and robust preventive measures, hospitals like Johns Hopkins exemplify TQM's commitment to ensuring patient safety and overall organizational resilience.
Conclusion:
Total Quality Management continues to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of healthcare by fostering a culture of continuous improvement and excellence. Through patient-centered care, process improvement, employee involvement, data-driven decision-making, and preventive measures, hospitals can enhance not only the quality of services but also the overall patient experience. By learning from successful examples, healthcare organizations can further embrace TQM principles to create a sustainable framework for delivering high-quality care in an ever-evolving landscape.






















Comments