Unveiling the Power of Lean Management: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- islam Arid

- Apr 25, 2024
- 7 min read
Updated: Nov 12, 2024
Lean management has become a universal management tool for delivering value and optimizing workflows. Explore the Lean methodology along with its benefits and find examples.
The premise to organize a work process so that waste is minimized, and resources are utilized at optimal capacity while keeping productivity turned Lean management into a universal management tool embraced across industries. Rooted in three simple ideas: always seeking improvement, creating value, and eliminating waste, let’s learn more about the concept. We’ll discuss Lean management’s origin and principles, its benefits, and disadvantages, and look into examples.
Lean Management Definition
Lean or Lean management is a business approach for maximizing customer value while minimizing waste. It is based on the principles of the Toyota Production System (TPS) and aims to create a culture of continuous improvement in an organization. The main goal of Lean management is to improve efficiency and effectiveness by reducing the time spent on non-value-adding activities and optimizing the flow of work. Such waste in Lean can include overproduction, waiting time, unnecessary transportation, excess inventory, unnecessary processing, and defects. The Lean concept is successfully applied to any business or production process, from manufacturing to healthcare, engineering, and software development.
The Birth of Lean Management
Lean was derived from Lean Manufacturing and Toyota Production System methods around 70 years ago. In the late 1940s, when Toyota put the foundations of Lean manufacturing, they aimed to reduce processes that don’t bring value to the product. By doing so, they succeeded in achieving significant improvements in productivity, efficiency, cycle time, and cost efficiency. The success of the TPS at Toyota led to the spread of Lean thinking and the implementation of Lean principles around the world. Today, Lean management is used in a wide range of industries and organizations and has evolved to include a variety of tools, techniques, and approaches.
Indeed, the term "lean production" was made up by John Krafcik (former CEO of Google’s self-driving car project Waymo) in his 1988 article "Triumph of the Lean Production System". His studies formed the data behind James P. Womack’s 1990 book "The Machine That Changed the World: The Story of Lean Production".
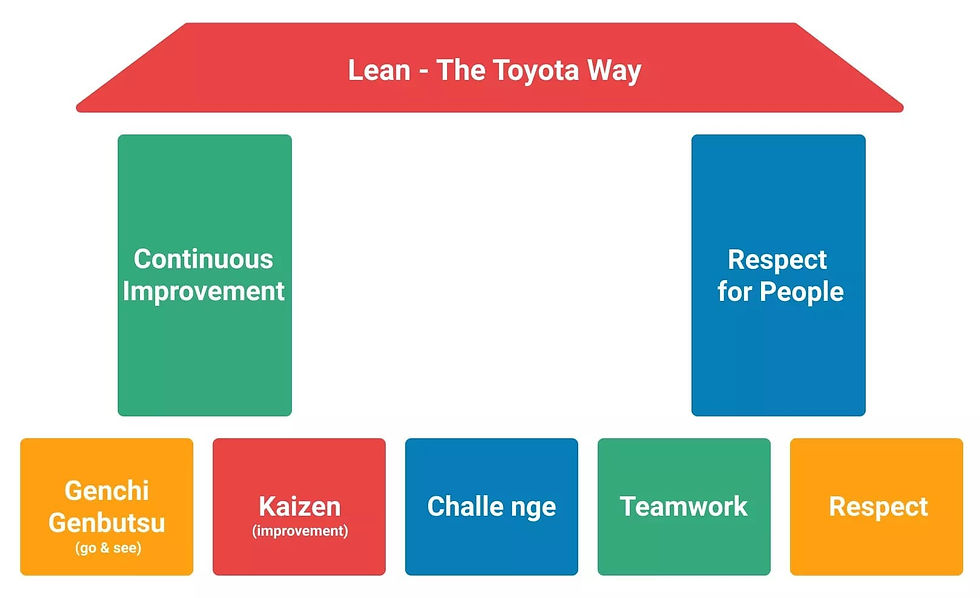
What Are the Building Blocks of Lean Management?
Lean management emphasizes the importance of respecting and empowering employees and encourages the development of a culture of problem-solving and continuous improvement. The two pivotal Lean pillars are indeed respect for people and a mindset of continuous improvement. The Lean improvement methodology aims to provide a structural approach to continuously improve work processes, purposes, and people. Instead of holding total control of work processes and keeping the spotlight, Lean management encourages shared responsibility and shared leadership. After all, a good idea or initiative can be born at any level of the hierarchy, and Lean trusts the people who are doing the job to have the final say.
What Are the 5 Lean Management Principles?

1. Identify Value
What does every company strive to do? To offer a product or service that a customer is ready to pay for. To do so, a company needs to add value defined by its customers’ needs.
The value lies in the problem you are trying to solve for the customer. More specifically, in the part of the solution that your customer is actively willing to pay. Any other activity or process that doesn’t bring value to the product is considered a waste.
In Lean value is the first thing you need to identify. So, first, decide what you want to deliver, then move on to the next step.
2. Value Stream Mapping
This is the point where you literally need to map the workflow of your company. It should include all actions and people involved in delivering the product to the customer. By doing so, you will be able to identify what parts of the process bring no value.
Applying the Lean principle of value stream mapping will show you where value is being generated and in what proportion different parts of the process do or do not produce value.
When you have your value stream mapped, it will be much easier for you to see which processes are owned by what teams and who is responsible for measuring, evaluating, and improving those processes. This big picture will enable you to detect the steps that don’t bring value and eliminate them.
3. Create a Continuous Workflow
After you master your value stream, you need to make sure that each team's workflow remains smooth. Keep in mind that it may take a while.
Developing a product or service will often include cross-functional teamwork. Bottlenecks and interruptions may appear at any time. However, by breaking down work into smaller batches and visualizing the workflow, you can easily detect and remove process roadblocks.
4. Create a Pull System
Having a stable workflow guarantees that your teams can deliver work tasks much faster with less effort. However, in order to secure a stable workflow, make sure to create a pull system when it comes to the Lean methodology.
In such a system, the work is pulled only if there is a demand for it. This lets you optimize resources’ capacity and deliver products or services only if there is an actual need.
Let’s take a restaurant, for example. You go there and order a pizza. The baker pulls your order and starts making your pizza. He doesn’t prepare tons of dishes in advance because there isn’t actual demand, and these tons of dishes can turn into a waste of resources.
5. Continuous Improvement
After going through all the previous steps, you have already built your Lean management system. However, don’t forget to pay attention to this last step, probably the most important one.
Remember, your system is not isolated and static. Problems may occur with any of the previous steps. This is why you need to make sure that employees on every level are involved in continuously improving the process.
There are different techniques to encourage continuous improvement. For example, every team may have a daily stand-up meeting to discuss what has been done, what needs to be done, and possible obstacles - an easy way to process improvements daily.
What Are the Benefits of Lean Management?
Lean management can help organizations and teams alike to create a stable work system with a higher chance of improving overall performance. Here's a list of the major advantages you can benefit from when introducing Lean.
Increased employee engagement and focus: Lean encourages employees to identify and solve problems leading to increased engagement and focus on activities that bring value.
Improving productivity and efficiency: By eliminating waste and streamlining processes, Lean management can help organizations become more efficient and productive, allowing them to produce more with the same or fewer resources.
Faster time to market: By establishing a pull system, a Lean management system helps organizations to deliver work only if there is actual demand and reduces their lead times.
Improved quality: Lean management places a strong emphasis on identifying and eliminating defects, which can help to improve product and service quality.
Continuous improvement: Lean management is built on a culture of continuous improvement, enabling organizations to adapt to changing market conditions and stay competitive over the long term.
Common Challenges When Implementing Lean Management
While Lean management has many benefits, it is important to also consider the potential disadvantages, which can include:
Resistance to change: Implementing a lean management system can be a significant change for an organization and may be met with resistance from employees who are used to more traditional ways of working.
Difficulties in implementation: Implementing a lean management system can be complex and challenging, requiring significant investment in training, infrastructure, and culture change.
Risk of over-focusing on data: Lean management relies heavily on data and metrics to measure performance, which can lead to a focus on short-term results at the expense of long-term goals or strategic planning.
Lean Management Examples
Lean Software Development
In 2003, Mary and Tom Poppendieck published their book "Lean software development: an Agile Toolkit". The book describes how you can apply the initial principles of the Lean methodology to software development.
At the end of the day, Lean software development comes down to 7 principles. In the beginning, it didn’t gain popularity, but a few years later, it became one of the most popular software development methods.
The Lean Startup
Eric Ries, an engineer and serial entrepreneur, developed a methodology based on the Lean principles to help startups succeed. In 2011, he packed his ideas into a book called "The Lean Startup". The concept consists of 5 basic principles that aim to help startups be more flexible and responsive to changes.
From a business point of view, Lean is to shorten product development cycles and rapidly discover if a given business concept is viable. This methodology is also employed by government structures, marketing professionals, and others.
Lean Accounting
Lean accounting refers to the application of Lean management principles, such as a focus on delivering value to the customer and waste reduction to managing financial practices and processes. The approach allows organizations to streamline their operations and align them with the strategic goals of the organization.
Furthermore, by promoting Lean thinking in accounting, companies can make financial information easier to understand and more relevant across an organization’s teams and departments.
Lean Management Applied in Healthcare
Lean management principles find an increasing application in healthcare institutions to improve patient care, service quality, healthcare workers’ satisfaction, and cost-effectiveness.
Lean Management Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What Are the 5 Lean Management Principles?
The five guiding principles of Lean management include:
Identifying value
Mapping the entire value creation process
Creating a continuous workflow
Establishing a pull work system
Seeking continuous improvement
What Are the 3 Foundational Ideas of Lean Management?
The three driving forces behind the Lean management concept are creating customer value, reducing waste, and always looking for ways to improve.
What Are the Different Tools of Lean Management?
Some of the most common lean tools used by organizations and teams new to the Lean philosophy include:
Value-stream mapping (VSM) - for visualization, analysis, and improvement of all the steps in a product or service delivery process.
5 Whys root cause analysis – for uncovering the root cause of process bottlenecks and constraints.
Kanban – for defining, managing, and improving services that deliver knowledge work.
5S method – for workspace optimization to reduce waste and streamline processes.






















Comments